Lab11
Introduction
In this lab I perform localization with the Bayes filter on your actual robot. We only use the update step based on full 360 degree scans with the ToF sensor. The point of the lab is to appreciate the difference between simulation and real-world systems.
The result of this lab is pretty good, which provides a solid foundation to carry on Lab12.
Tasks
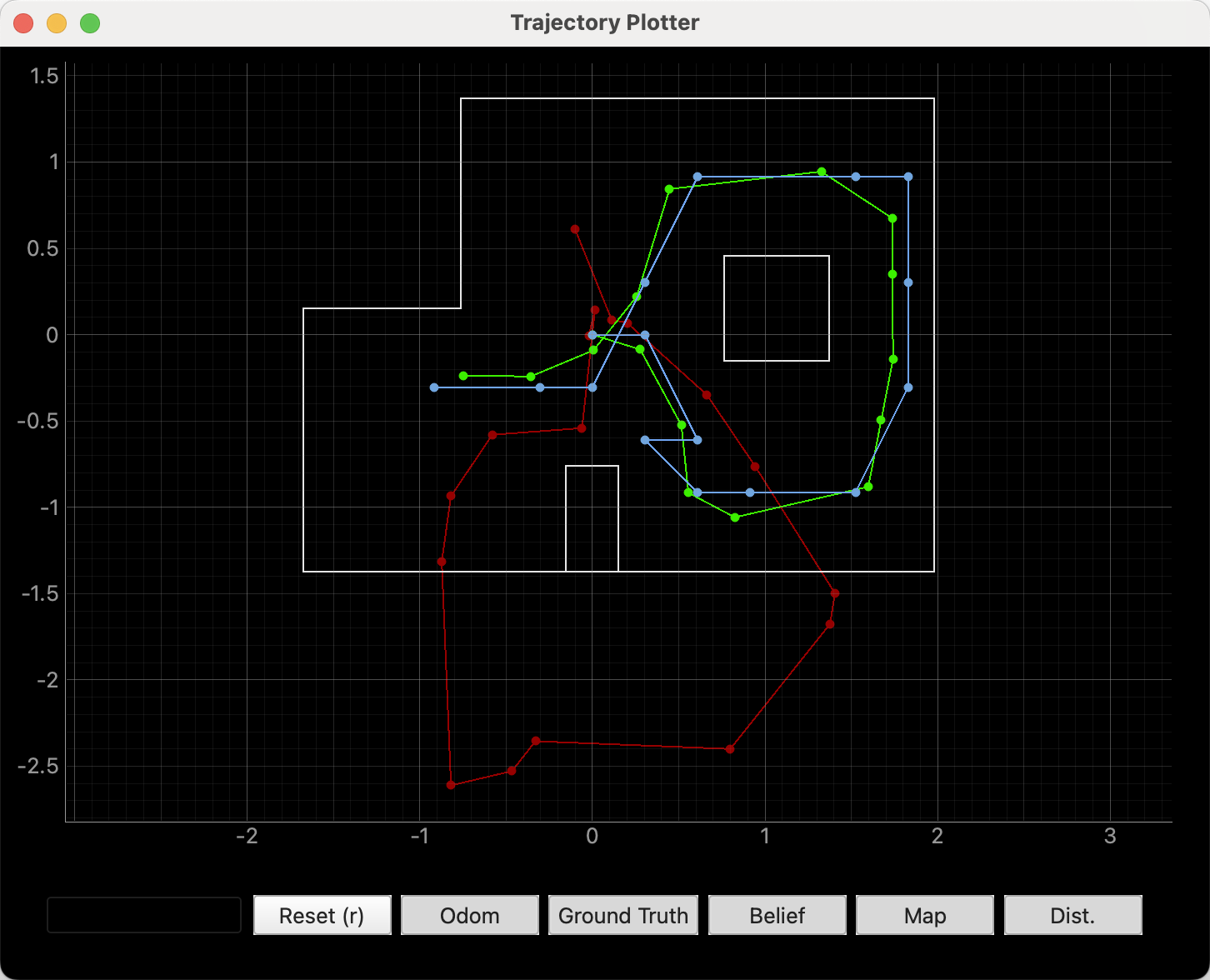
1. Test Localization in Simulation: Run the notebook lab11_sim.ipynb and attach a single screenshot of the final plot (odom, ground truth and belief).
2. Using a uniform prior on the pose, run (only) the update step using the sensor measurement data to localize your robot
a) Implement member function perform_observation_loop of class RealRobot
def perform_observation_loop(self, rot_vel=120):
timestamps_ms = []
distances = []
yaws = []
scanning = True
transfering = True
def notification_handler(uuid, byte_array):
nonlocal scanning
nonlocal transfering
ss = ble.bytearray_to_string(byte_array)
if ss.count('|') < 2:
print(ss)
if ss == "Scan End":
scanning = False
elif ss == "Transfer End":
transfering = False
return
idx, data = ss.split(':')
timestamp, distance, yaw = data.split('|')
timestamps_ms.append(int(timestamp))
distances.append(int(distance))
yaws.append(int(yaw))
observations_count = 18
self.ble.start_notify(ble.uuid['RX_STRING'], notification_handler)
self.ble.send_command(CMD.START_AUTO, "")
while scanning:
print("scanning")
asyncio.run(asyncio.sleep(1))
self.ble.send_command(CMD.GET_HISTORY_DATA, "")
while transfering:
print("transfering")
asyncio.run(asyncio.sleep(1))
ble.stop_notify(ble.uuid['RX_STRING'])
sensor_ranges = np.divide(np.array(distances), 1000)[np.newaxis].T
sensor_bearings = np.array(yaws)[np.newaxis].T
print(sensor_ranges.T)
print(sensor_bearings.T)
return sensor_ranges, sensor_bearings
b) Place robot in all four marked poses and run the update step of the Bayes filter
I tested all four marked poses:
- -3, -2
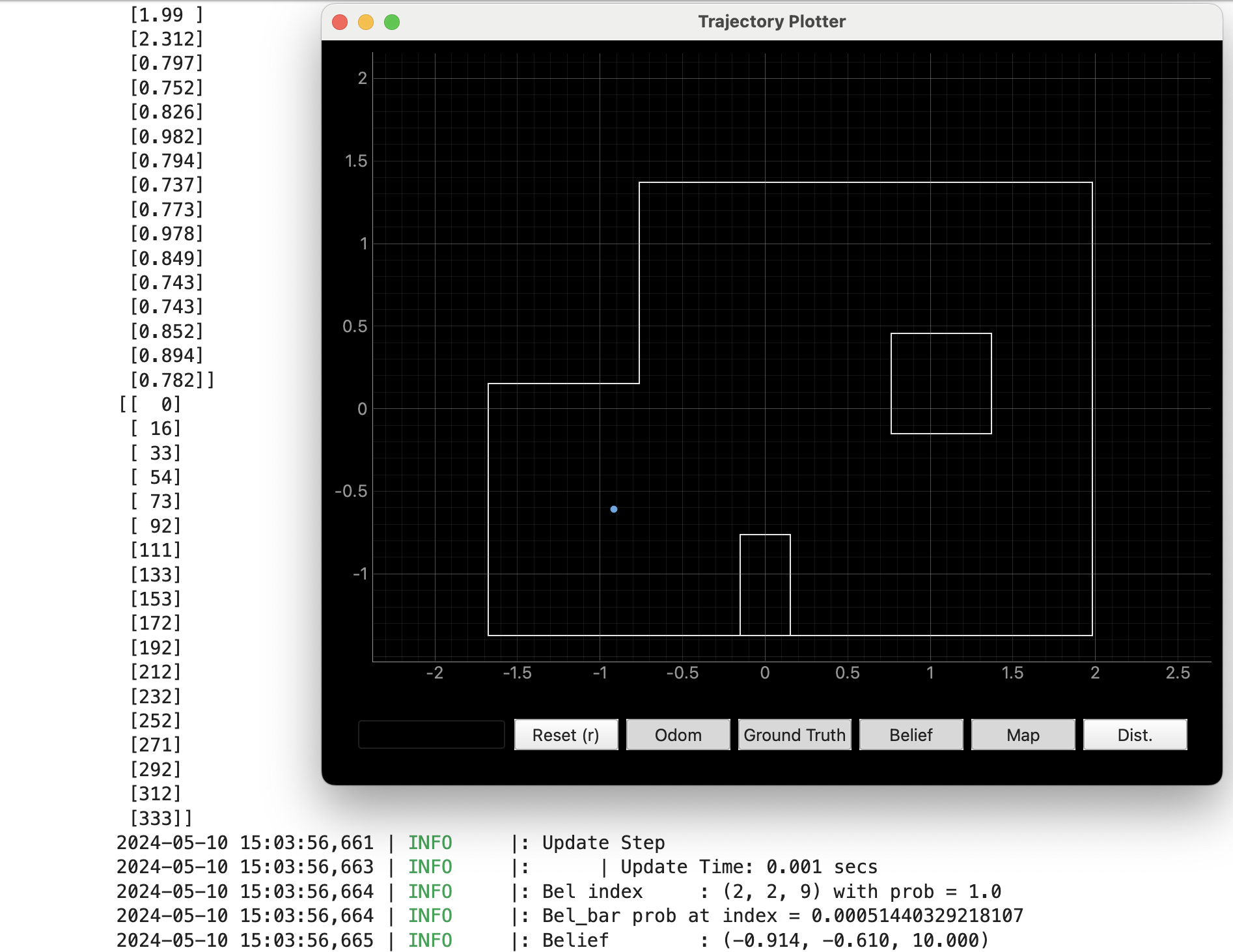
This result given by bayes filter is exactly the same as grond truth.
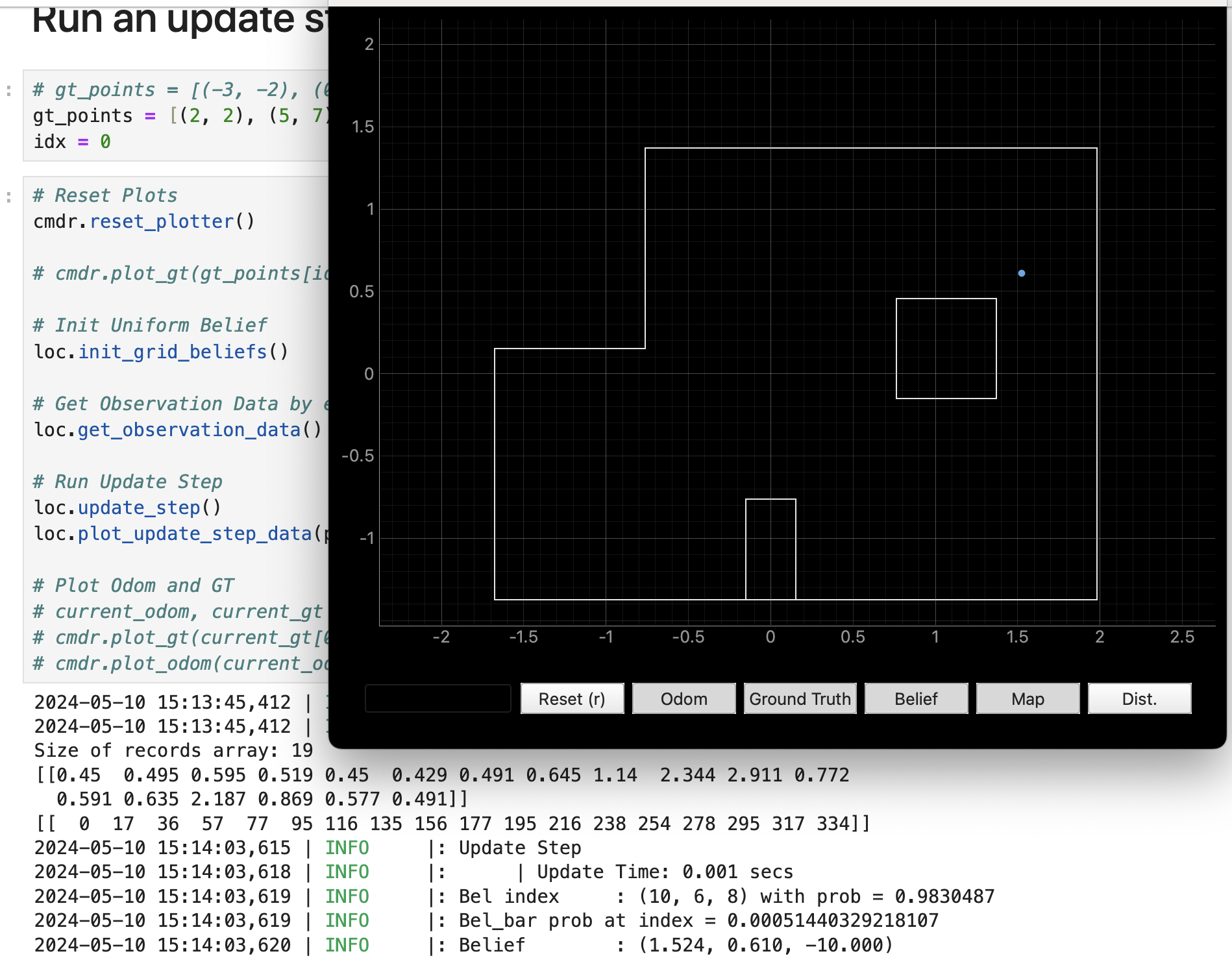
- 0, 3
This result given by bayes filter is exactly the same as grond truth.
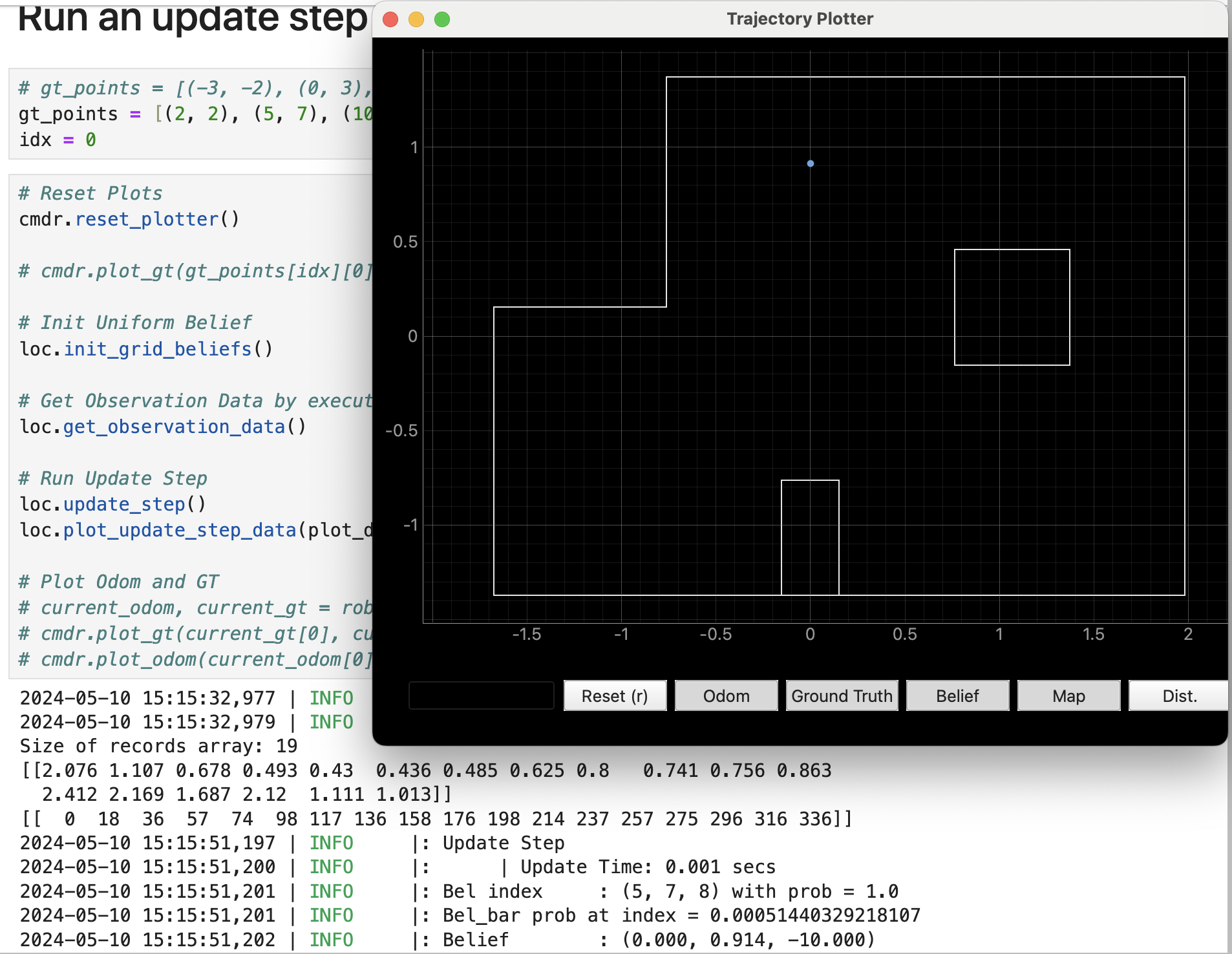
- 5, 3
This result given by bayes filter is (5, 2), which is one block away from the ground truth (5, 3). But not bad anyway.
- 5, -3
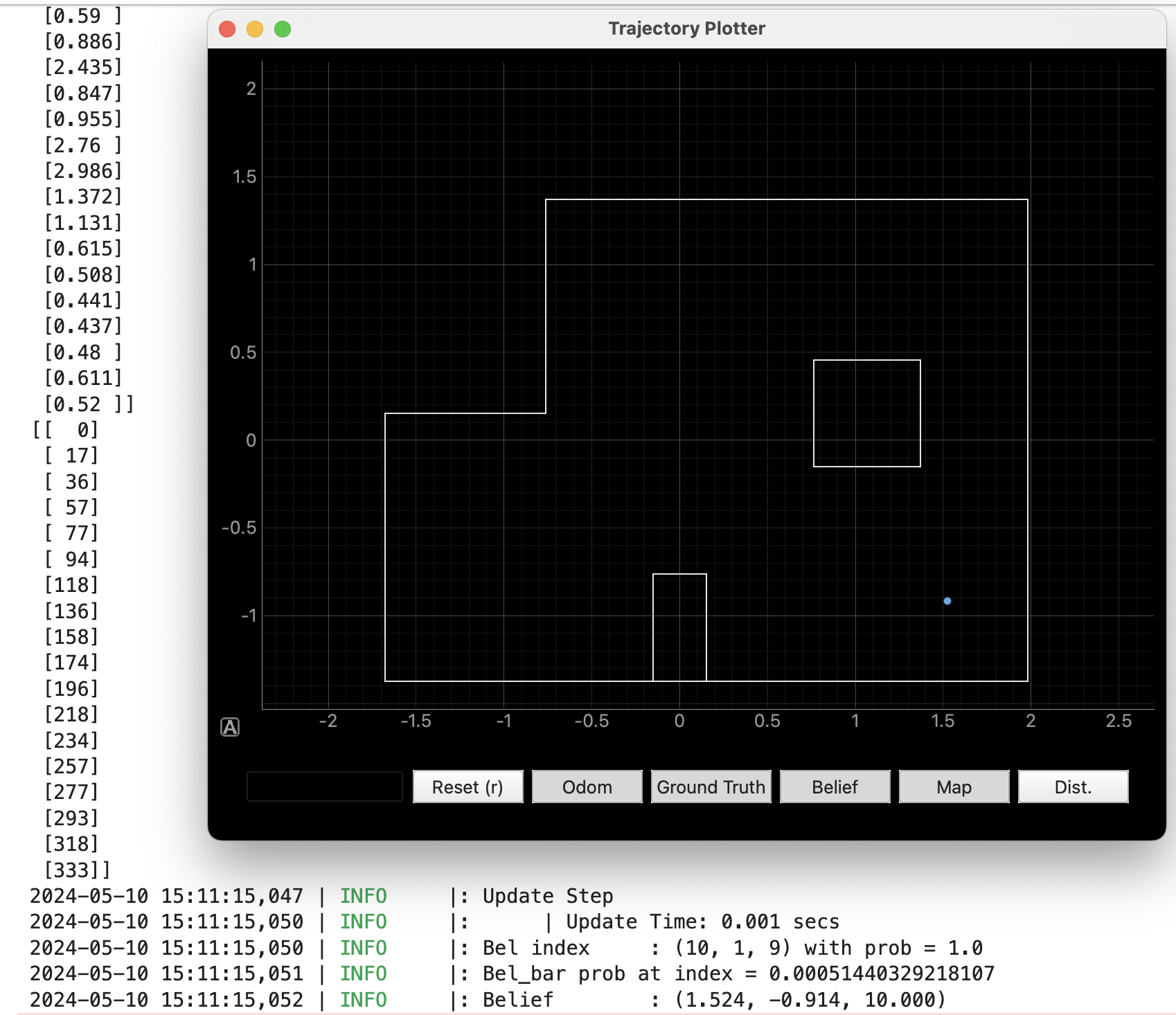
This result given by bayes filter is exactly the same as grond truth.
The video of robot working at pose (5, -3) is attached below:
Discussion
How close is the localized pose w.r.t to the ground truth?
In conclusion, 3 of the 4 marked pose give perfect estimation through bayes filter, 1 has an error of one block, which is also good enough.
Does the robot localize better in certain poses? If so, why?
No, it performs almost equally well in all tested poses on my robot.